Research
Mechanisms that underlie pancreatic organogenesis and diseases
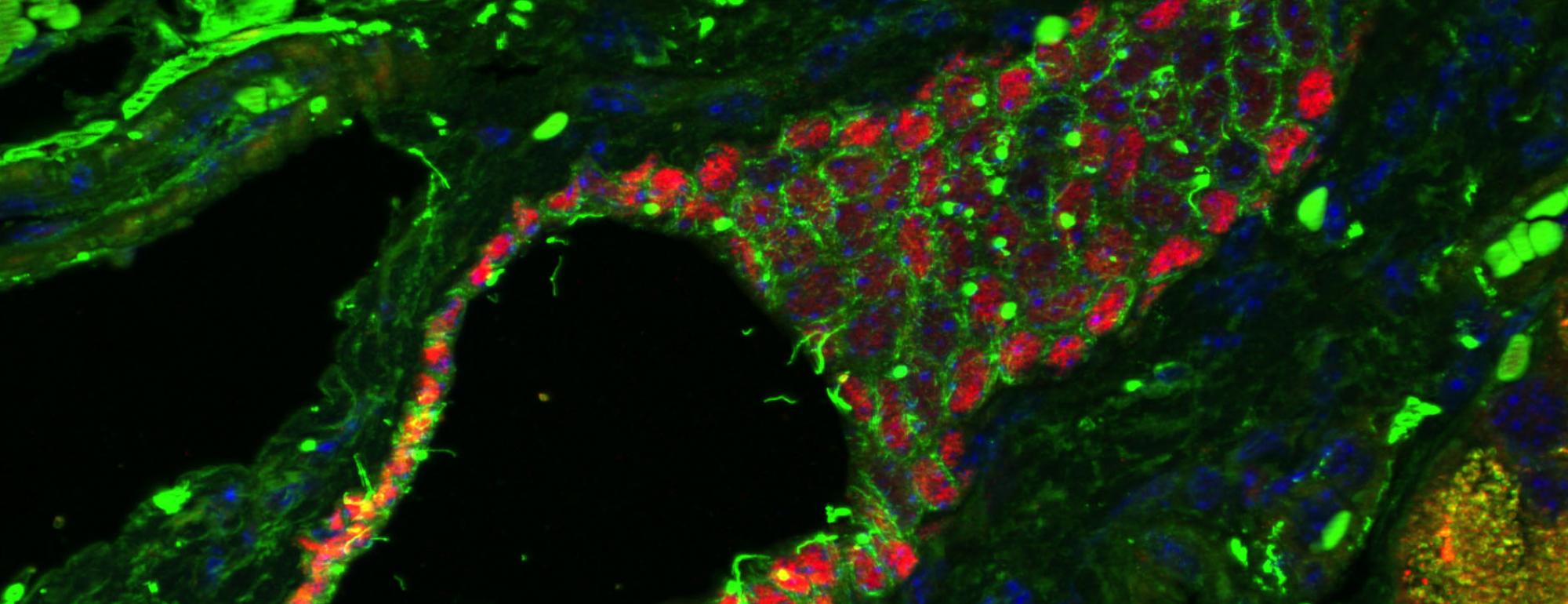
Our aims are to determine whether controlled activation and deactivation of particular signaling pathways affect the function, proliferation and/or survival of insulin-producing β-cells, promote the formation of β-cells from uncommitted stem cells, and prevent the formation and growth of pancreatic tumors.
To address these questions, we are currently using multiple tools including transgenic mouse models in which gene expression is conditionally regulated to manipulate the activity of specific signaling pathways. The information gained from these studies is used to optimize and develop novel methods to generate functional insulin-producing β-cells from human stem cell populations such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and induced pluripotentstem (iPS) cells.